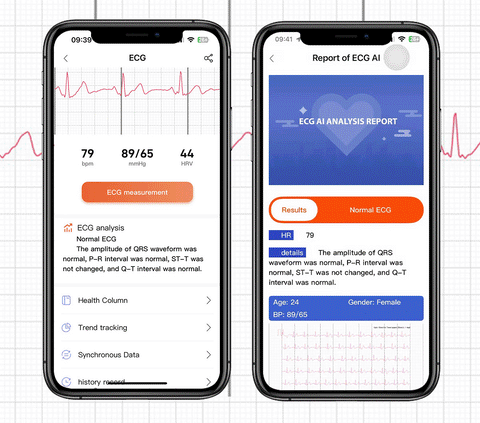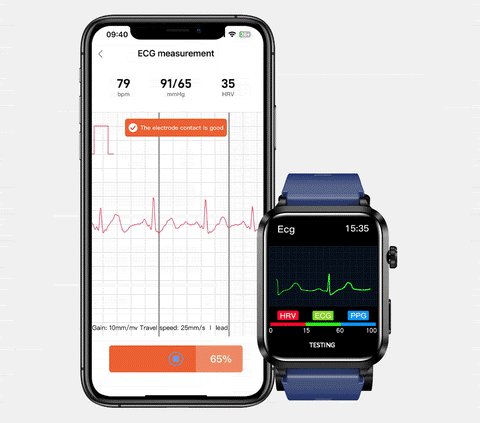
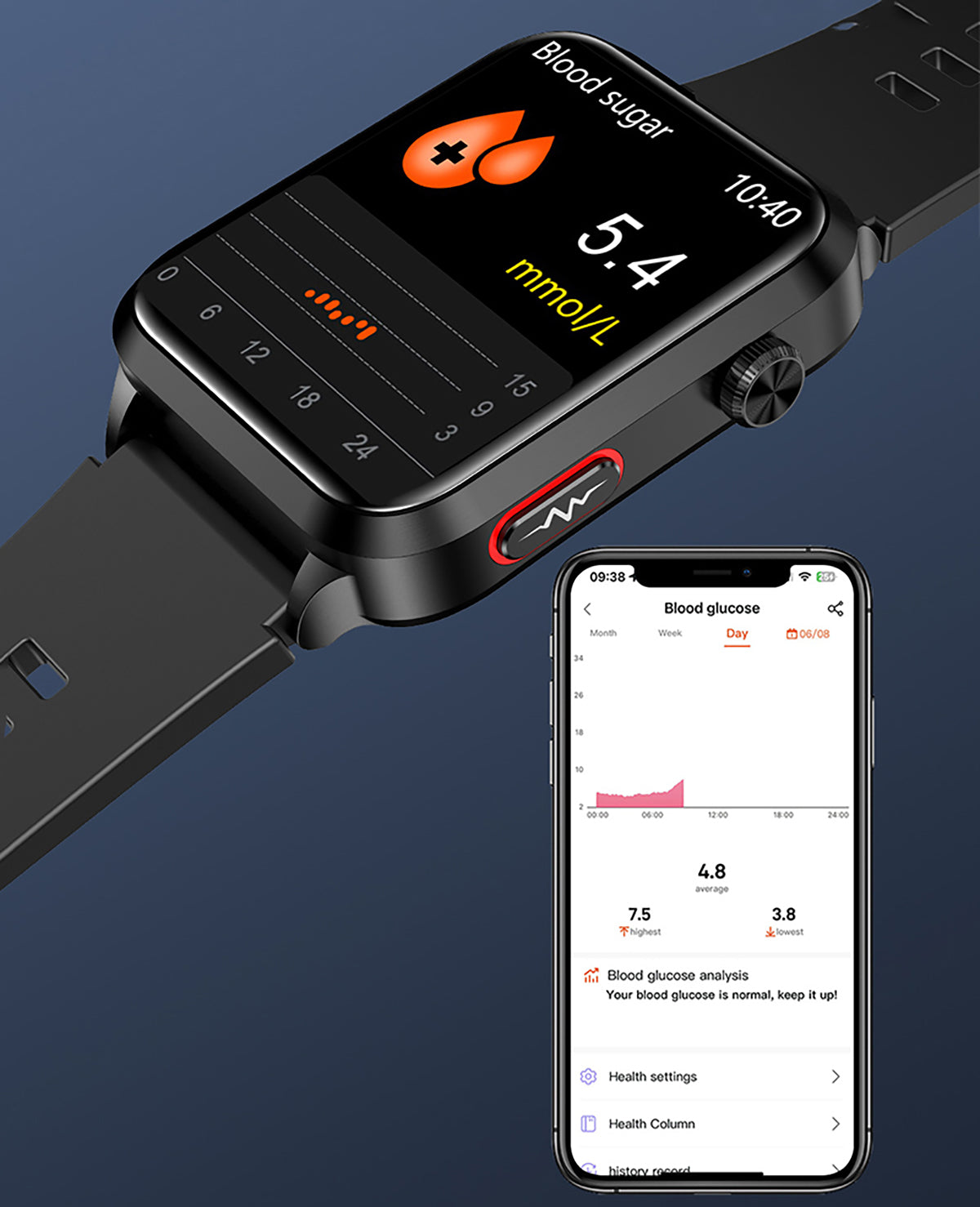
Blood Sugar Monitor
Sleep, an essential component of our daily routine, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Beyond its restorative effects, sleep patterns and quality have a profound impact on blood sugar control, making it a pivotal factor in diabetes management. In this blog, we delve into the intricate relationship between sleep and diabetes, shedding light on why a good night's sleep is paramount for those navigating the challenges of blood sugar regulation.
Understanding the Link: Sleep and Blood Sugar
-
Nightly Restoration: Adequate sleep is synonymous with nightly restoration. During the various sleep stages, the body undergoes repair, regeneration, and hormone regulation. One such hormone affected is insulin, a key player in blood sugar management. Disruptions in sleep patterns can lead to insulin resistance, making it harder for cells to respond to insulin effectively.
-
Cortisol, Stress, and Glucose: Sleep deprivation elevates cortisol levels, the body's primary stress hormone. Increased cortisol triggers the liver to release more glucose into the bloodstream, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. For individuals with diabetes, this presents a significant challenge in maintaining optimal glucose control.
The Impact on Diabetes Management:
-
Insulin Sensitivity: Quality sleep enhances insulin sensitivity, ensuring that the body's cells respond efficiently to insulin signals. This heightened sensitivity is pivotal for individuals with diabetes, as it aids in better blood sugar control.
-
Glycemic Control: Consistent sleep patterns contribute to stable glycemic control. Irregular sleep can lead to blood sugar spikes and dips, complicating diabetes management. Establishing a consistent sleep routine can positively influence these fluctuations.
Practical Tips for Improved Sleep and Blood Sugar Control:
-
Prioritize Sleep Hygiene: Cultivate a sleep-friendly environment by ensuring a comfortable bed, minimizing noise and light, and maintaining a cool room temperature.
-
Establish a Routine: Aim for a consistent sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at the same time daily. This helps regulate circadian rhythms, promoting better sleep quality.
-
Mindful Eating: Be cautious about late-night snacking, particularly on sugary or high-carbohydrate foods. Opt for balanced snacks if needed to avoid disrupting blood sugar levels during sleep.
-
Limit Stimulants: Reduce caffeine and nicotine intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. These stimulants can interfere with falling asleep and impact sleep quality.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity, but try to complete intense workouts several hours before bedtime. Exercise promotes better sleep quality and aids in blood sugar control.
- The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Integrating technology into diabetes management can provide valuable insights into the impact of sleep on blood sugar levels. Continuous Glucose Monitoring allows individuals to track real-time glucose trends, helping identify patterns influenced by sleep.
Conclusion: A Night of Quality Sleep, A Day of Better Blood Sugar Control
Recognizing the intricate interplay between sleep patterns, quality, and blood sugar control is paramount for individuals managing diabetes. By prioritizing healthy sleep habits, embracing consistent routines, and making lifestyle adjustments, one can unlock the potential for improved blood sugar management. Quality sleep isn't just a luxury; it's a powerful tool in the arsenal against diabetes, contributing to overall health and vitality.
When you need a tool that can continuously monitor your blood sugar, check out the BP Doctor Med 14. It has the function of monitoring blood sugar, which can help you assess the risk of hyperglycemia and predict vascular health in advance.